Glossary: What is Asthma
Asthma is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulties in breathing. In this glossary, we will explore the fundamental aspects of asthma, including its understanding, types, diagnosis, treatment, and the experiences of living with this condition.
Understanding Asthma
Definition and Overview
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to become inflamed and constricted. This condition can lead to recurring episodes of wheezing, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. The severity of asthma can vary between individuals and can change over time, making effective management crucial.
Understanding asthma involves considering various environmental and genetic factors that contribute to its development. While it can develop at any age, it often begins in childhood. Some individuals may experience symptoms only occasionally, while others may have frequent and severe attacks that require immediate medical attention. The unpredictability of asthma can be particularly challenging for those affected, as it often requires careful monitoring and adjustments in lifestyle to maintain control over the condition.
Additionally, the emotional and psychological impact of living with asthma cannot be overlooked. Many individuals with asthma report feelings of anxiety or fear related to their symptoms, especially during physical exertion or in environments where triggers are present. This emotional burden can further complicate the management of asthma, making it essential for patients to have a support system and access to mental health resources.
Causes of Asthma
The causes of asthma can be multifactorial. They typically include a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors. Common triggers for asthma symptoms may include allergens like pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander, and tobacco smoke.
Moreover, physical activity, especially in cold or dry air, respiratory infections, and even strong emotions such as stress can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Understanding these triggers is crucial for effective management and can help prevent asthma attacks. In recent years, researchers have also begun to explore the role of air pollution and climate change as significant contributors to the increasing prevalence of asthma, particularly in urban areas where exposure to pollutants is higher.
In addition to environmental factors, certain occupational exposures have been linked to asthma development. Jobs that involve exposure to irritants or allergens, such as construction, agriculture, and healthcare, may increase the risk of developing asthma or worsening existing symptoms. Awareness of these occupational hazards is vital for prevention and management strategies, particularly for individuals in high-risk professions.
Common Symptoms
Asthma symptoms can manifest in various ways and may differ between individuals. The most common symptoms include:
- Wheezing: This high-pitched whistling sound occurs during breathing, especially when exhaling.
- Coughing: Persistent cough, especially at night or early in the morning, is a common symptom.
- Shortness of breath: Individuals may experience difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest tightness: This feeling can resemble pressure or discomfort in the chest.
Recognizing these symptoms early on is essential for prompt treatment and to minimize the impact of asthma on daily life. It is also important to note that asthma symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency, with some individuals experiencing periods of remission where symptoms are minimal or absent. Keeping a symptom diary can be a useful tool for patients and healthcare providers to identify patterns and triggers, leading to more personalized and effective management plans.
Furthermore, the impact of asthma extends beyond physical symptoms. Many individuals may experience limitations in their daily activities, such as exercise, work, or social interactions, due to fear of an asthma attack. This can lead to a decreased quality of life and increased feelings of isolation. Therefore, addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of asthma is crucial for comprehensive care and support for those affected by this chronic condition.
Types of Asthma
Childhood Asthma
Childhood asthma is the most common form of asthma and typically begins in early years of life. Although many children may outgrow their symptoms, some continue to experience asthma into adulthood. Managing childhood asthma involves regular monitoring and working with healthcare providers to ensure that children can maintain an active lifestyle.
Parents often play a critical role in identifying triggers and making necessary adjustments in the home environment to reduce allergy exposure and irritants that could provoke symptoms. For instance, maintaining a clean living space, using air purifiers, and minimizing exposure to tobacco smoke can significantly improve a child's respiratory health. Additionally, educating children about their condition empowers them to recognize early signs of an asthma attack and take appropriate action, such as using their inhaler or avoiding specific triggers.
Adult-Onset Asthma
Adult-onset asthma occurs after puberty and can be triggered by various factors, including respiratory infections, allergies, and occupational exposures. This type of asthma may not present with the typical symptoms associated with childhood asthma, making diagnosis more challenging.
In adults, symptoms might be less predictable and can sometimes be more severe. It is essential for adults to recognize changes in their respiratory health and seek a professional diagnosis to manage their symptoms effectively. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity and physical inactivity, can also exacerbate asthma symptoms in adults. Therefore, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet can play a crucial role in managing adult-onset asthma and improving overall lung function.
Occupational Asthma
Occupational asthma is a form of asthma triggered or exacerbated by workplace exposures. Common irritants include chemical fumes, dust, and allergens present in various workplaces. This condition highlights the importance of recognizing workplace environments that may contribute to asthma symptoms.
Individuals with occupational asthma may need to make adjustments to their work environments or consider alternative employment options to reduce exposure to triggers. Collaborating with occupational health specialists can also provide insights on managing symptoms effectively. Moreover, employers have a responsibility to ensure a safe working environment, which may involve implementing better ventilation systems, providing personal protective equipment, and conducting regular health assessments for employees. Awareness and education about occupational asthma can lead to proactive measures that not only protect workers but also promote a healthier workplace culture.
Diagnosing Asthma
Medical History and Physical Exam
Diagnosing asthma typically starts with a thorough medical history and a physical examination. Healthcare providers will inquire about the frequency and severity of symptoms as well as any potential triggers. Understanding family history is also crucial, as asthma can run in families. Additionally, providers may ask about environmental factors, such as exposure to tobacco smoke, pollution, or occupational hazards, which can exacerbate asthma symptoms. This detailed history helps paint a clearer picture of the patient's condition and potential risk factors.

A physical examination will focus on respiratory function. Providers may listen to lung sounds and check for any abnormalities while assessing overall health. They might also evaluate the patient's breathing patterns and look for signs of respiratory distress, such as wheezing or prolonged expiration. This initial evaluation plays a significant role in determining if further testing is needed, as well as establishing a baseline for future assessments.
Lung Function Tests
Lung function tests, or spirometry, measure how much air the lungs can hold and how quickly it can be expelled. This testing helps assess the degree of airway obstruction and can provide concrete evidence of asthma. These tests are often conducted before and after the patient uses an inhaler to gauge responsiveness to bronchodilators. The results can help determine not only the presence of asthma but also its severity, guiding treatment options.
These measurements help to confirm a diagnosis of asthma and evaluate its severity. It’s vital for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and schedule regular spirometry tests to monitor their condition over time. Consistent monitoring can reveal changes in lung function and help tailor treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most effective care based on their current status.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
Sometimes, healthcare providers may recommend additional tests to rule out other conditions and refine the asthma diagnosis. These tests can include:
- Peak Flow Monitoring: This technique measures how fast air is expelled from the lungs and helps track asthma control at home. Patients can use a peak flow meter to record their readings, which can be invaluable for identifying patterns and potential flare-ups.
- Allergy Testing: Identifying allergens that may contribute to asthma symptoms can be beneficial in managing triggers. Skin prick tests or blood tests can help pinpoint specific sensitivities, allowing for targeted avoidance strategies and treatment.
- Exhaled Nitric Oxide Test: This measures the amount of nitric oxide in a person’s breath, which can indicate inflammation in the airways. Elevated levels may suggest poorly controlled asthma and can prompt adjustments in medication.
Overall, a comprehensive approach to diagnosis is crucial for effective asthma management. By combining clinical assessments with objective testing, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient. This thorough diagnostic process not only aids in the management of asthma but also empowers patients with knowledge and strategies to better control their condition, leading to improved quality of life.
Treatment and Management of Asthma
Medications for Asthma
Treatment for asthma typically involves a combination of medications to control symptoms and prevent attacks. There are two primary types of medications:
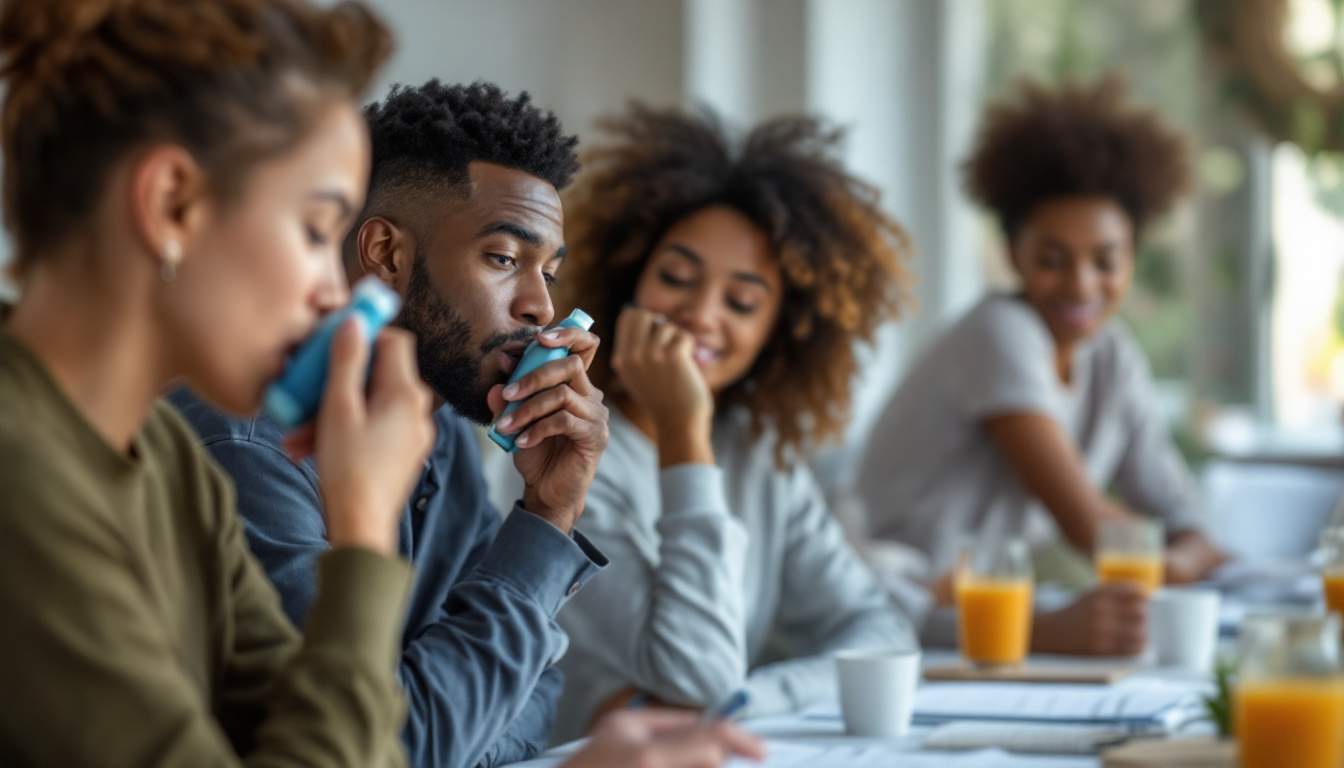

- Long-Term Control Medications: These are taken daily to manage chronic symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. Examples include inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers.
- Quick-Relief Medications: Also known as rescue inhalers, these medications provide immediate relief during an asthma attack and are used as needed.
It’s essential for individuals with asthma to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique symptoms and triggers. Regular follow-ups can help in adjusting the medication as needed, ensuring optimal control of the condition. Additionally, understanding how to properly use inhalers and other delivery devices is crucial, as incorrect usage can lead to ineffective treatment. Educational resources and training sessions can empower patients to take charge of their asthma management.
Lifestyle Changes for Asthma Management
Beyond medications, lifestyle changes are critical in managing asthma effectively. Some suggested adjustments include:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and mitigating exposure to known triggers is essential for preventing symptoms.
- Staying Active: Regular exercise can improve lung function and overall health, but individuals should consult their healthcare provider for individualized advice.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity can exacerbate asthma symptoms, so focusing on a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can help.
These adjustments can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively and improve quality of life. Additionally, incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga or mindfulness can be beneficial, as stress is a known trigger for many asthma sufferers. Environmental modifications, such as using air purifiers and hypoallergenic bedding, can also create a more asthma-friendly living space. Engaging in community support groups can provide emotional encouragement and practical tips from others who understand the challenges of living with asthma.
Emergency Care for Asthma Attacks
In some cases, asthma attacks can escalate quickly and require immediate intervention. Recognizing the signs of a severe asthma attack is crucial—these may include increased shortness of breath, trouble speaking, or a blue tint around the lips or face.
During an asthma attack, individuals should use their quick-relief inhaler immediately and seek emergency medical assistance if symptoms do not improve. Creating an asthma action plan with a healthcare provider can help guide individuals and their families during emergencies. This plan typically outlines steps to take when symptoms worsen, including when to use medications and when to seek emergency help. Educating family members and friends about the signs of an asthma attack and how to assist can be invaluable, ensuring that support is readily available in times of need. Additionally, keeping a record of peak flow readings can help in monitoring lung function and predicting potential exacerbations, allowing for proactive management of the condition.
Living with Asthma
Impact on Daily Life
Living with asthma can pose challenges in various aspects of life, including sleep, physical activity, and overall well-being. Many individuals find that managing asthma requires planning and organization, especially in social situations or during exercise. For instance, the unpredictability of asthma attacks can lead to anxiety, making it difficult to engage in spontaneous activities or travel without thorough preparation. This often means carrying inhalers and medications at all times, as well as being aware of potential triggers in different environments, such as pollen, smoke, or strong odors.
However, with effective management and support, many people with asthma lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the condition and making informed decisions about lifestyle choices can greatly enhance quality of life and reduce the impact of asthma on daily activities. Individuals often learn to adapt their routines, such as incorporating breathing exercises or using air purifiers at home, which can help minimize symptoms and create a more comfortable living space. Furthermore, many find that engaging in low-impact exercises, like swimming or yoga, not only helps improve lung function but also contributes positively to mental health.
Coping Strategies and Support
Coping with asthma involves not only managing physical symptoms but also addressing emotional and psychological aspects. Support groups, counseling, and educational resources can provide valuable assistance. Many healthcare providers recommend joining local or online support networks where individuals can share their experiences and coping strategies. These groups often host workshops and seminars that educate members about the latest asthma management techniques and research, fostering an environment of continuous learning and support.
Connecting with other individuals who have asthma can foster a sense of community and understanding. Many people find comfort in sharing their experiences and learning from each other’s strategies for managing their condition. Additionally, family and friends play a crucial role in this support system; educating them about asthma can help create a more understanding environment, where loved ones are aware of triggers and can assist during an asthma attack. This network of support not only alleviates feelings of isolation but also empowers individuals to advocate for their health needs in various situations.
Future Research and Developments in Asthma Treatment
Research into asthma is continually evolving, leading to new and innovative treatment options. Advances in biotechnology and personalized medicine are paving the way for more targeted therapies that may improve asthma control and reduce side effects. For example, biologic therapies that target specific pathways involved in asthma inflammation are showing promise in clinical trials, offering hope to those with severe asthma who have not responded well to traditional treatments. These advancements could potentially transform the approach to asthma management, allowing for more tailored and effective treatment plans.
As scientists continue to investigate the underlying mechanisms of asthma, there is hope for new treatments that will enhance the lives of those living with this chronic condition. Staying informed about these developments can empower individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. Furthermore, ongoing research into environmental factors and lifestyle interventions is crucial, as it may lead to preventive strategies that can reduce the incidence of asthma in future generations. Engaging with healthcare professionals about emerging research and treatment options can help individuals make informed decisions about their asthma management and overall health journey.
In conclusion, asthma is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. With the right knowledge and support, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges of living with asthma, achieving a better quality of life.
If you're looking to take control of your asthma and enhance your quality of life, Alveo's innovative Continuous Respiratory Wearable might be the breakthrough you need. With features like real-time respiratory monitoring, personalized breathing routines, and insights into how the environment affects your breathing, Alveo is designed for comfort and tailored to your unique lung capacity. Don't miss out on the opportunity to transform your asthma management. Sign up on our waiting list today and breathe easier with Alveo's cutting-edge technology.