Understanding VO2 Max and Why It Matters
VO2 Max, or maximal oxygen consumption, represents the maximum rate at which your body can use oxygen during intense exercise. This metric is essential for assessing cardiovascular fitness, often reflecting overall physical health as well. The term "VO2 Max" combines "V" for volume, "O2" for oxygen, and "max" for maximum—together indicating how much oxygen your body can utilise efficiently. A higher VO2 Max typically signifies better stamina, as your body can take in more oxygen and produce more energy to power the muscle cells during exercise. This makes VO2 Max a critical factor for anyone looking to boost endurance and fitness.
Historically, VO2 Max measurement was primarily reserved for athletes, but recent advances in wearable technology and an increased focus on health optimisation have made it more widely accessible. Now, VO2 Max is recognised as an important health metric for anyone, helping users monitor and improve their aerobic fitness and health outcomes.
How Breathing Affects VO2 Max
Enhancing VO2 Max is often linked to the efficiency of oxygen intake, transport, and utilisation throughout the body. By practicing specific breathing techniques (see below), you can improve lung function and strengthen respiratory muscles such as the diaphragm. Methods like nasal breathing and controlled deep breathing increase oxygen intake by maintaining higher concentrations in the lungs, which supports more effective gas exchange.
In addition to respiratory benefits, these breathing exercises enhance cardiovascular function by improving blood circulation, enabling more oxygen-rich blood to reach muscles. This improved cardiovascular efficiency helps increase VO2 Max and enhances endurance during intense activities.
Wearable Technology for Accurate VO2 Max Tracking
Wearable technology has revolutionised VO2 Max measurements, making them more accurate and accessible. Traditional methods of measuring VO2 Max in a lab setting, such as cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET), are often costly and complex. However, new technologies, including seismocardiography (SCG), are changing this. For example, the VentriJect Seismofit device claims to use SCG to measure VO2 Max without exercise, making accurate VO2 Max assessments more accessible to the general public. This technology can assess cardiorespiratory fitness faster and more affordably than traditional methods.
Cambridge researchers have also pioneered methods that allow wearable devices to estimate fitness levels without requiring physical activity, using sophisticated algorithms that claim to deliver lab-level accuracy. For individuals who want to optimise their training results, choosing wearables equipped with these advanced technologies is essential. While lab-based methods remain the gold standard, wearables are quickly evolving to offer convenient, reliable, and data-rich insights into fitness progress.
The Best Breathing Techniques to Improve VO2 Max
1. Nasal Breathing
Nasal breathing, where you inhale and exhale exclusively through your nose, helps maximise oxygen efficiency. By breathing through the nose, the air is filtered, warmed, and humidified, which can reduce strain on the lungs and improve the oxygenation process. Studies suggest that due to the lower respiratory rate associated with nasal breathing, there is more time for oxygen diffusion. This enhanced diffusion can compensate for the reduced airflow through the nasal passages and help maintain adequate oxygenation even at high exercise intensities.
2. Diaphragmatic Breathing
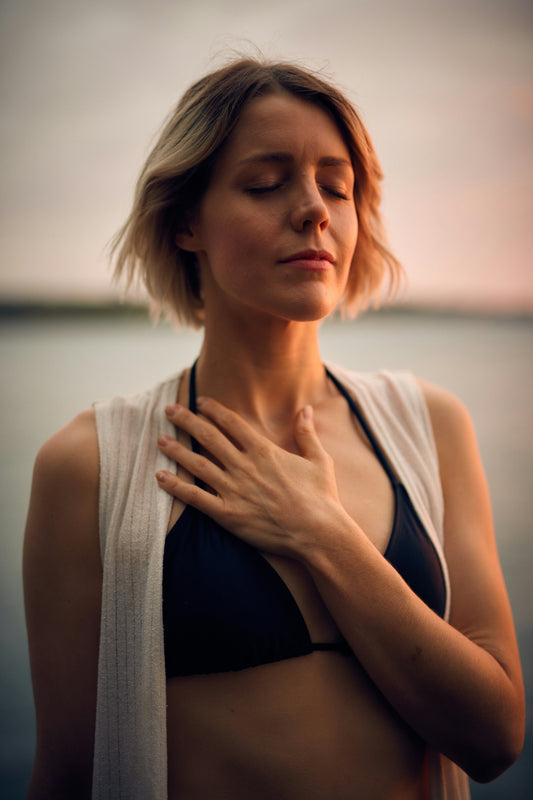
Also known as belly breathing, this technique engages the diaphragm, promoting deeper, fuller breaths that improve oxygen exchange. Diaphragmatic breathing is simple to practice: place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen, focusing on moving only your abdomen during each breath. Over time, this technique strengthens the diaphragm, making it easier to sustain deep breathing during high-intensity exercise and improve VO2 max.
3. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) with Breath Control
HIIT alternates between short bursts of intense activity and periods of rest, challenging your cardiovascular and respiratory systems. When paired with focused breathing exercises, HIIT can improve oxygen efficiency, boost VO2 Max, and support better cardiovascular health.
Respiratory Muscle Training: A Game-Changer for VO2 Max
Respiratory muscle training focuses on strengthening the muscles involved in breathing, such as the diaphragm and intercostals. By specifically targeting these muscles, individuals can improve their VO2 Max, allowing for more efficient oxygen usage and better endurance. Techniques that pair respiratory muscle training with exercises like HIIT have been shown to enhance both oxygen efficiency and stress management, contributing to improved fitness and sleep quality. Over time, these exercises can be invaluable in helping to maximise VO2 Max, endurance, and overall performance.
Choosing the Right Wearable for Tracking VO2 Max
Modern wearable devices, including Apple Watch, Garmin, and Fitbit, now feature VO2 Max tracking capabilities. These devices use heart rate monitors, accelerometers, and proprietary algorithms to estimate VO2 Max, enabling users to monitor and improve their cardiorespiratory fitness. For instance, Garmin’s VO2 Max calculations use data from running and cycling activities, offering insights into both aerobic and anaerobic capacity.
While wearables are a convenient solution for tracking fitness, the accuracy of VO2 Max readings may vary. It’s essential to understand the limitations and potential variances based on activity level and conditions. Nonetheless, by consistently using wearables, users can benefit from more personalised, data-driven training plans.