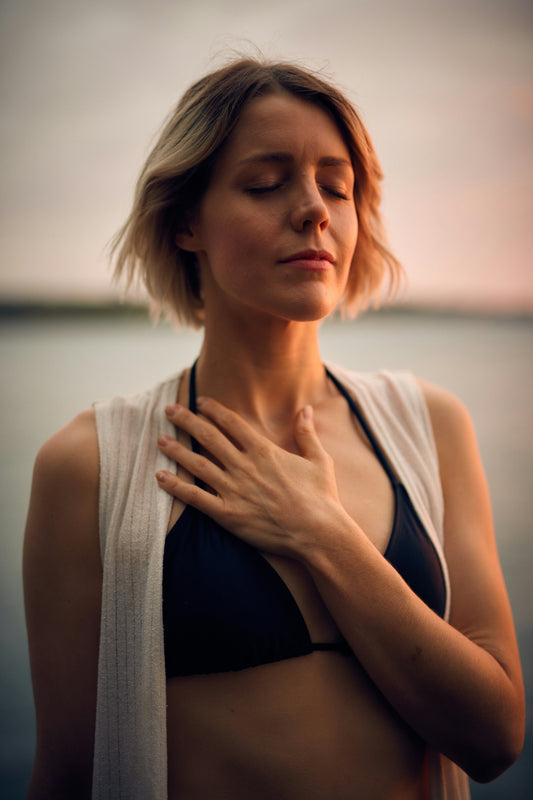
Are you looking to increase your lung capacity and boost your overall respiratory health? In this article, we’ll cover simple but powerful exercises that can help you breathe more effectively. By making these exercises part of your daily routine, you’ll strengthen your lungs and improve how well they function.
Why is Lung Capacity Important?
Lung capacity is the maximum amount of air your lungs can hold, which directly affects how well oxygen is delivered throughout your body and how efficiently carbon dioxide is removed. Improving lung capacity can enhance your stamina, support better physical performance, and lead to overall improved health.
Simple Breathing Exercises to Boost Lung Capacity
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
- How it works: Diaphragmatic breathing involves using the diaphragm, a muscle below your lungs, to draw in a deeper breath. By fully engaging this muscle, you help expand your lungs and improve oxygen intake and lung efficiency.
- How to do it: Sit or lie down comfortably. Place one hand one your chest and one hand on your abdomen.Inhale slowly through your nose, letting your stomach rise as you fill your lungs with air. Exhale through your mouth, allowing your stomach to fall. Focus on slow, controlled breathing. The hand on your chest should not move while the hand on your abdomen will allow you to feel your breath.
2. Pursed-Lip Breathing
- How it works: Pursed-lip breathing helps keep your airways open for longer, making it easier to exhale fully and get rid of stale air.
- How to do it: Inhale deeply through your nose, then purse your lips as if you’re about to whistle. Exhale slowly and gently through your pursed lips, aiming for the exhale to last twice as long as the inhale. Repeat several times. Pursed lip breathing may feel awkward or uncomfortable at first. However, with regular practice, the technique will become easier.
3. Box Breathing
- How it works: Box breathing, also known as four-square breathing, is a technique that focuses on balanced breathing. It helps calm the nervous system, increase lung capacity, and improve focus.
- How to do it: Sit or stand comfortably with a straight posture. Inhale slowly through your nose for a count of four, hold the breath for another count of four, exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of four, and hold again for a count of four before the next inhale. Repeat several times, gradually increasing your hold times as you get comfortable.
4. Rib Stretch
- How it works: Stretching the muscles between your ribs allows for more flexibility in the chest, helping your lungs expand more fully with each breath.
- How to do it: Stand up tall with your hands on your hips. Take a deep breath in, then lean gently to one side to feel a stretch along your ribcage. Hold for a few seconds, return to the center, and repeat on the other side. This exercise promotes greater mobility in the rib area, aiding in deeper breaths.
Benefits of Regular Breathing Exercises

Including these simple exercises in your daily routine can offer a wide range of benefits:
Increased lung capacity by strengthening respiratory muscles, allowing you to take in more oxygen with each breath.
Improved oxygen flow to the brain and muscles, which can boost energy levels, mental clarity, and physical performance.
Enhanced endurance and stamina, especially helpful for athletes or anyone aiming to improve their physical fitness.
Reduced stress and anxiety by engaging in slow, mindful breathing, which activates the body’s relaxation response.
A Few Things to Keep in Mind
Regular practice is key to seeing benefits from these exercises. Try setting aside a few minutes each day, gradually increasing the time as you become more comfortable with each technique. Remember, it’s always a good idea to check with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
With consistent practice and a little patience, you’ll notice a difference in your lung capacity and overall breathing power, helping you enjoy the benefits of a healthier respiratory system.